Difference between revisions of "Segmented"
(shorten up to Mechanism section) |
m (cut down until ===Extended/Non-reducing===) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Adaptation== | == Adaptation== | ||
| − | For naturally Segmented sleepers, the adaptation is easy | + | For naturally Segmented sleepers, the adaptation is easy. For non-natural Segmented sleepers, adapting to Segmented may be harder than adapting to [[Siesta]] or [[E1]]. Waking up from the first core could be difficult. Boredom during the night gap can make it hard to stay awake. The second core sleep containing much REM sleep can also grogginess or dizziness upon waking. Over time, with strict adherence to the schedule, these issues should disappear. |
| − | + | ||
| + | After Segmented, there is a gradual adaptation route to [[Dual core]] schedules, and also [[Triphasic]], as the division of core sleeps had been learned. | ||
==Difficulty== | ==Difficulty== | ||
| − | The difficulty level of Segmented varies across individuals, and depends on the amount of sleep being scheduled. Overall, it is still considered a friendly schedule | + | The difficulty level of Segmented varies across individuals, and depends on the amount of sleep being scheduled. Overall, it is still considered a friendly schedule for beginners. |
| − | == | + | ==Variants== |
| − | While the | + | While the default dual 3.5 hour core variant has had the most success, a few other combinations are also plausible and have been adapted to in the past. Beginners can attempt these variants, with some precautions. |
| − | === | + | === 6-hour total sleep === |
| − | <gallery mode="packed-overlay" widths=" | + | <gallery mode="packed-overlay" widths="250" heights="250"> |
File:Segmented short 1.png|Segmented with 6h total sleep (Version 1) | File:Segmented short 1.png|Segmented with 6h total sleep (Version 1) | ||
File:Segmented short 2.png|Segmented with 6h total sleep (Version 2) | File:Segmented short 2.png|Segmented with 6h total sleep (Version 2) | ||
| − | </gallery>These are 2 | + | </gallery> |
| + | These are 2 modified variants that have reported some success over the years. Since the total sleep is only 6 hours, it may be suitable for those with slightly below average monophasic baselines (~7h). One problem with this schedule would be a circadian dip in the early afternoon hours, without naps to address them. Because more light sleep has been cut compared to the default variant, staying awake could be more difficult. | ||
| − | The wake gap between each core | + | The wake gap between each core should be at least 4 hours to cover the SWS and REM peaks more efficiently, as well as to reduce the length of the day gap. The overall adaptation may be more difficult than the standard version because of the reduced sleep time. The benefit is the added extra time at night, and only needing to sleep at night without using daytime naps. |
| − | The difference between 4.5-1.5 and 3-3 core distribution is that those with more SWS requirements can attempt the former option, while those | + | The difference between 4.5-1.5 and 3-3 core distribution is that those with more SWS requirements can attempt the former option, while those needing similar amounts of REM and SWS can pick the latter. Overall, the 3-3 variant better balances sleep stages, and has seen more success overall than the 4.5-1.5 variant. |
| − | ===Uneven core | + | ===Uneven core lengths=== |
| − | [[File:Segmented Uneven.png| | + | [[File:Segmented Uneven.png|right|thumb|A Segmented variant with uneven core lengths]] |
| + | This variant, which is rarely attempted, has cores of slightly different lengths. These variants allows for slightly more time awake, may be easier to schedule, without a significantly harder adaptation. Other plausible combinations include <u>3-3.5</u>, or even <u>4.5-2.5</u> and <u>5-1.5</u>. It would be helpful to know the SWS and REM requirements before picking any of these variants, though. | ||
| − | Generally, variants with a longer first core | + | Generally, variants with a longer first core allows for more alertness during core gap, and the second core does not need to be as long. However, the longer the first core, the less "DC-like" it becomes, meaning that the sleep stages becomes less distinctly allocated into the two cores. The longer first core may also resemble Siesta, with the second sleep looking like a daytime core sleep. |
===Late first core=== | ===Late first core=== | ||
| − | [[File:Segmented Late First Core.png| | + | [[File:Segmented Late First Core.png|right|thumb|Segmented with a late first core]] |
| + | Sleepers who would schedule this variant are expected to have low SWS needs, and/or a lot of polyphasic experience as well as the stringent management of food, exercise and lighting. This variant is not usually recommended, as the first core being away from SWS peak drastically increases the difficulty. Circadian management is recommended, as with other late-core schedules. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For this variant, the core gap can be smaller than the default, because of the higher SWS pressure prior to core 2. | ||
| − | |||
{{TNT|Segmented-ext}} | {{TNT|Segmented-ext}} | ||
===Extended/Non-reducing=== | ===Extended/Non-reducing=== | ||
| − | The | + | The difference between Segmented-extended and non-reducing Segmented is that the former can reduce some sleep for long sleepers, whereas the latter aims not to reduce any sleep (e.g, 4.5-4.5 core combo for 9h sleeper). The non-reducing variant is believed to resemble the historical sleep pattern in pre-industrial Europe. Both variants occupy hours in both evening and morning, which can then clash with many types of social commitments. |
| + | |||
| + | Compared to the default or other reducing variants, these two allow for some flexibility of either core, even during adaptation, and naturally segmented sleepers can adapt to the schedule by simply follow their natural patterns of tiredness. One success from the non-reducing variant (~6.5h total sleep on average) has the first core being ~4.5h long consistently while the second core hovers around 2h. This suggests that non-reducing variants can still be utilized by short sleepers to achieve a flexible Segmented schedule. For non-natural Segmented sleepers, it is still advisable to try to sleep at the same time everyday for each core sleep. | ||
| − | + | However, without reducing total sleep, it is expected that it will be significantly harder to fall asleep, which may contribute to the difficulty of the adaptation. | |
===Siesta-hybrid=== | ===Siesta-hybrid=== | ||
Revision as of 14:25, 13 December 2020
| Segmented | |
|---|---|
| chart link
Legend
| |
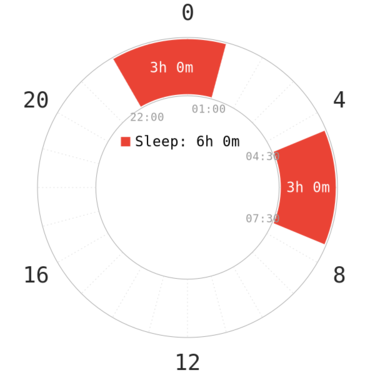
| Total sleep | 7 hours |
| Proposed by | None, used by humans throughout history. |
| Difficulty | Moderate |
| Specification | 2 long cores at night aligned to SWS and REM peaks respectively. |
Segmented is a biphasic schedule[1] with two cores at night, usually with a total sleep time close to one's personal monophasic baseline.
Origin
Segmented sleep, sometimes referred to as bifurcated or divided sleep, is one of the original polyphasic sleep patterns. It is the basis of the Dual core schedule line. In its non-reducing form, it is believed to have been practiced by some human societies since time immemorial until the advent of electric lighting . In short photoperiods (fewer daylight hours), it has been shown that human sleep is naturally segmented[2].
People would often go to bed some time after sunset, wake up after a few hours, stay awake for a couple hours, and then go back to bed until sunrise. Some naturally Segmented sleepers report interrupted monophasic sleep, where they wake up in the middle of the night. They are often suggested to adopt a Segmented sleep schedule.
Mechanism
The Polyphasic Discord Community has discovered some possible mechanics of Segmented sleep. The basis of Segmented sleep is the sleep peaks. During the early hours of the night (~21-24), when natural melatonin secretion starts, SWS can be gained efficiently. In EEG readings of adapted sleepers, the first core sleep is usually dense in SWS, whereas the second core sleep contains primarily REM sleep. The divided core sleeps are thus denser in vital sleep stages, and allow for a small cut in total sleep with stable sleep times. Naps in the day are not needed because the amount of light sleep cut is small enough, and the day gap is also substantially shortened compared to a monophasic schedule.
Both core sleeps are scheduled to be 3.5 hours by default because the sleep cycles are known to lengthen to about 105 minutes from the approximately 90-minute cycles on monophasic sleep. This would also explain the viability of the schedule despite having fewer cycles.
The wake gap between each core should at least 90 minutes, with a longer gap recommended (~2.5-3 hours) for non-natural Segmented sleepers. The reason for this is to prevent the cores from becoming interrupted sleep, in which there is a only a brief period of awakening during sleep, before the sleeper goes back to sleep, which disrupts the sleep cycle and drastically reduces sleep quality.
Staying awake for at least ~90m will usually prevent this, so that the second core starts in a new sleep cycle. A wake gap that is too short is unlikely to be productive time, and it may also be difficult to fall asleep as not enough sleep pressure has been accumulated. The original default recommendation was 2 hours of gap, but has since been changed to 3 hours as some people were unable to fully adapt to the 2-hour gap version.
Adaptation
For naturally Segmented sleepers, the adaptation is easy. For non-natural Segmented sleepers, adapting to Segmented may be harder than adapting to Siesta or E1. Waking up from the first core could be difficult. Boredom during the night gap can make it hard to stay awake. The second core sleep containing much REM sleep can also grogginess or dizziness upon waking. Over time, with strict adherence to the schedule, these issues should disappear.
After Segmented, there is a gradual adaptation route to Dual core schedules, and also Triphasic, as the division of core sleeps had been learned.
Difficulty
The difficulty level of Segmented varies across individuals, and depends on the amount of sleep being scheduled. Overall, it is still considered a friendly schedule for beginners.
Variants
While the default dual 3.5 hour core variant has had the most success, a few other combinations are also plausible and have been adapted to in the past. Beginners can attempt these variants, with some precautions.
6-hour total sleep
These are 2 modified variants that have reported some success over the years. Since the total sleep is only 6 hours, it may be suitable for those with slightly below average monophasic baselines (~7h). One problem with this schedule would be a circadian dip in the early afternoon hours, without naps to address them. Because more light sleep has been cut compared to the default variant, staying awake could be more difficult.
The wake gap between each core should be at least 4 hours to cover the SWS and REM peaks more efficiently, as well as to reduce the length of the day gap. The overall adaptation may be more difficult than the standard version because of the reduced sleep time. The benefit is the added extra time at night, and only needing to sleep at night without using daytime naps.
The difference between 4.5-1.5 and 3-3 core distribution is that those with more SWS requirements can attempt the former option, while those needing similar amounts of REM and SWS can pick the latter. Overall, the 3-3 variant better balances sleep stages, and has seen more success overall than the 4.5-1.5 variant.
Uneven core lengths
This variant, which is rarely attempted, has cores of slightly different lengths. These variants allows for slightly more time awake, may be easier to schedule, without a significantly harder adaptation. Other plausible combinations include 3-3.5, or even 4.5-2.5 and 5-1.5. It would be helpful to know the SWS and REM requirements before picking any of these variants, though.
Generally, variants with a longer first core allows for more alertness during core gap, and the second core does not need to be as long. However, the longer the first core, the less "DC-like" it becomes, meaning that the sleep stages becomes less distinctly allocated into the two cores. The longer first core may also resemble Siesta, with the second sleep looking like a daytime core sleep.
Late first core
Sleepers who would schedule this variant are expected to have low SWS needs, and/or a lot of polyphasic experience as well as the stringent management of food, exercise and lighting. This variant is not usually recommended, as the first core being away from SWS peak drastically increases the difficulty. Circadian management is recommended, as with other late-core schedules.
For this variant, the core gap can be smaller than the default, because of the higher SWS pressure prior to core 2.
| Segmented-extended | |
|---|---|
| chart link
Legend
| |
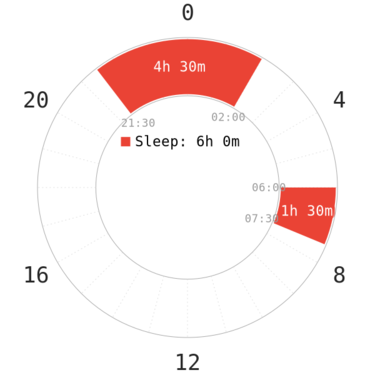
| Total sleep | 7.5 - 8 hours |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| Specification | 2 cores, aligned to SWS and REM peaks. |
Extended/Non-reducing
The difference between Segmented-extended and non-reducing Segmented is that the former can reduce some sleep for long sleepers, whereas the latter aims not to reduce any sleep (e.g, 4.5-4.5 core combo for 9h sleeper). The non-reducing variant is believed to resemble the historical sleep pattern in pre-industrial Europe. Both variants occupy hours in both evening and morning, which can then clash with many types of social commitments.
Compared to the default or other reducing variants, these two allow for some flexibility of either core, even during adaptation, and naturally segmented sleepers can adapt to the schedule by simply follow their natural patterns of tiredness. One success from the non-reducing variant (~6.5h total sleep on average) has the first core being ~4.5h long consistently while the second core hovers around 2h. This suggests that non-reducing variants can still be utilized by short sleepers to achieve a flexible Segmented schedule. For non-natural Segmented sleepers, it is still advisable to try to sleep at the same time everyday for each core sleep.
However, without reducing total sleep, it is expected that it will be significantly harder to fall asleep, which may contribute to the difficulty of the adaptation.
Siesta-hybrid
This variant has surprisingly recorded at least 2 successes over time up to date; one attempt was done in a winter, where photoperiod was short. The first core becomes a lot shorter than usual, being reduced all the way to only 1 cycle, while the second core is dramatically longer than usual to compensate for the first core. Similar ideas can apply to 2.5-4.5 core distribution or so. The idea behind this variant is to have a very long wake gap between each core so that the second core can still occupy a fair amount of REM peak hours while still giving out sufficient SWS. The main concern is that since it is impossible for an average sleeper with at least 90m SWS to meet all SWS in the first core, the second core will have to provide the remaining SWS, and pushing the second core to very late hours at night may increase the difficulty of the process. Sleepers with lower SWS requirements or want to sleep less around evening hours can attempt this variant. However, as with a very unorthodox scheduling and the excessively long dark period, it will be tricky to make this Segmented variant work. This variant also takes away most, if not all social time in the evening; social time will have to be traded with the long wake gap between cores depending on personal preference.
Alternatively, Segmented can be scheduled with one core at night and one core in the day. Only a success or two have been reported thus far. This variant looks like Siesta with a long daytime core, and both core sleeps miss out on the peaks. The dark period should be 2-3h before the night core, and continue for ~2h after this core to stabilize the circadian rhythm. Adaptations are rare and a lot more difficult than a regular Segmented schedule, because skipping both sleep peaks can greatly hinder quality sleep. Over the course of adaptation, staying awake during the graveyard and morning hours will be tough, and having a long sleep in the day immediately can shake up the current sleep habits, if they are very different from this scheduling (e.g, regular 7-8h monophasic exclusively at night, non-nappers). The personal sleep peaks may change with artificial melatonin onset as a result of this new Segmented habits, however this entrainment will likely require an extended period of time for the circadian rhythm to be completely rotated.
Third shift
Very little is known about this scheduling method, and adaptations have been overall not rewarding. The nature of third shift often brings about changes in many health aspects, including higher risks for cardiovascular diseases, increased stress, lowered immune system and hypertension in the long run, including a monophasic pattern. Adapting to a Segmented pattern without the natural habit will result in a very risky adaptation. There have been at least a couple failures while deploying Segmented sleep for shift work, however, success is very rare, only a case or two. The idea is to have a core sleep right after the work period, and a core sleep before work. The plan on paper sounds compelling, but the adaptation process is far from easy.
Lifestyle Considerations
Given the extremely versatile ways of scheduling Segmented, there is a reason that Segmented sleep remains popular nowadays and has been succeeded by many polyphasic sleepers, from the most basic beginners to the most experienced veterans. A lot of brand new polyphasic sleepers often reflect on their inability to sleep in one chunk on monophasic sleep, and perpetually wake up in the middle of the night. The perfect solution would then be to start a Segmented adaptation as a result of the abrupt awakening. Thus, Segmented sleep would greatly benefit these groups of population.
Before one transitions to Segmented, it is very important to plan ahead what to do during the wake gap between 2 cores. This is very important because it is a critical component that can sway the adaptation to one's favor, should they know how to utilize the waking hours here. It is true that staying awake lonely at night when everyone else is sleeping and especially having nothing interesting to do can quickly become a daunting task to stay awake for many hours straight. For naturally segmented sleepers, this is not a big problem, but for non-segmented sleepers, there are a few tips to optimize these hours:
- Make a list of what activities or tasks that can only be achieved at night time or much better done at night than in the day. Take advantage of the silence of the night. This includes entertainment activities (e.g, watching TV shows), studying (after the first core) to revise the learned materials prior to the first core. Entertainment is fair game if you have not had a chance to enjoy them properly for a while. Being alone can also be an advantage at times.
- Dedicate to self-care. Self-care involves a lot of things, and it’s always a good thing to look after yourself when you have been too tired from working and committing to other obligations in the daytime. Self-care is also a great way to relieve built-up stress and anxiety. Autogenic training, meditation, yoga and stretching all come to mind. Just a brief session of 30-45m will help. Self-care isn’t something exclusive to Dual Core sleep - it can be utilized on any polyphasic schedules as well.
- Plan your next day or day(s). Planning activities is often the activity that takes the most amount of time if you fully craft out what you have to do in the day. In the roles of CEOs, managers and probably even interns and students, you will have a lot to work on and be concerned about. With clear planning comes clear execution of tasks - the worst thing of being on a polyphasic schedule is not being able to utilize the promising extra waking hours you gain from your hard-work adaptation. Thus, time management is key and if you think hard enough, I don’t think you run out of things to do.
In addition, there are massive advantages of Segmented that set it apart from other biphasic schedules. First, there is no need for a nap during the day. This effectively enthrones Segmented as the only schedule that can support more than 12h continuously staying awake without having to lie down for any shuteyes. In the modern society, this is an insurmountable perk that other polyphasic schedules cannot match. The seemingly endless wake gap allows for planning of several social events, even activisms, or any mainstream jobs that do not allow for any naps in the day. This is a fantastic way to adapt to Segmented sleep and enjoy the long daytime wake gap just like any monophasic sleepers.
Second, since Segmented does offer a decent amount of sleep, it is very viable to schedule the first core at ~11-11:30 PM (dark period begins at approximately 10 PM) to schedule a bit more evening events without having to sleep too early. The only thing to note, is that the late first core likely will delay the start time of the second core, so it is important to look at the second core and see if it will interfere with indispensable morning commitments. Under normal scheduling, however, there will be more limited evening social time on Segmented sleep.
Third, Segmented sleep can become flexible after adaptation. However, the flexibility records of Segmented is more humble than those of E1. Certain experienced sleepers or sleepers who go through a moderately challenging/easy adaptation to Segmented have shown their ability to flex at least one core sleep. Being able to flex the core sleeps allows for the absolute freedom in controlling the amount of waking hours between each core to suit one's schedule depending on days. For example, on certain days with nothing much to do, the core gap can shrink down a bit, so that the second core can start earlier than usual. Likewise, if there are more required tasks that need to be completed during this wake gap, the second core can be delayed a bit, or the first core can start earlier than usual. Lastly, the resilience of Segmented sleep also allows it to absorb some damages in scheduling, such as a party night, by delaying the first core to after the party and starting the second core some time after that. After adaptation, it should not take long to recover from such abrupt changes in sleep times, as long as these do not happen too often.
Fourth, Segmented sleep can support a lot of physical exercises, although like other schedules, it can be burdensome to keep the intense exercising habits while adapting. This can be remedied by having a longer first core and a shorter second core to increase the mobility of SWS gain. After the adaptation is complete, exercise intensity can increase again to match the previous level.
Lastly, the second core sleep on Segmented is often safe from real life interruptions and is often considered a REM stock for lucid dreaming. A lot of vivid dreaming experiences have been reported on the schedule over the years, most of which come from this second core. As an added bonus, this core (often long enough), can fix some inconsistencies or hiccups in sleep quality from the first core (e.g, interruptions in the middle, higher sleep onset than usual).
In spite of all the powerful advantages, Segmented seems at a disadvantage compared to other biphasic schedules when attempted by underage individuals, mostly those who are not natural Segmented sleepers. It may be possible that these individuals are better off with a long, continuous core sleep rather than segmented core sleeps, which can be a reason for quite a few incomplete adaptations.
- ↑ polyphasic.net. Retrieved 23-11-2020.
- ↑ https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1365-2869.1992.tb00019.x